Diving into the realm of Understanding income statements, we embark on a journey that unravels the mysteries behind financial statements and their crucial significance in the business world. Get ready to explore the ins and outs of income statements in a way that will leave you enlightened and empowered.
From decoding the language of finance to deciphering the clues hidden within the numbers, this topic promises to equip you with the knowledge needed to navigate the complex landscape of income statements with confidence.
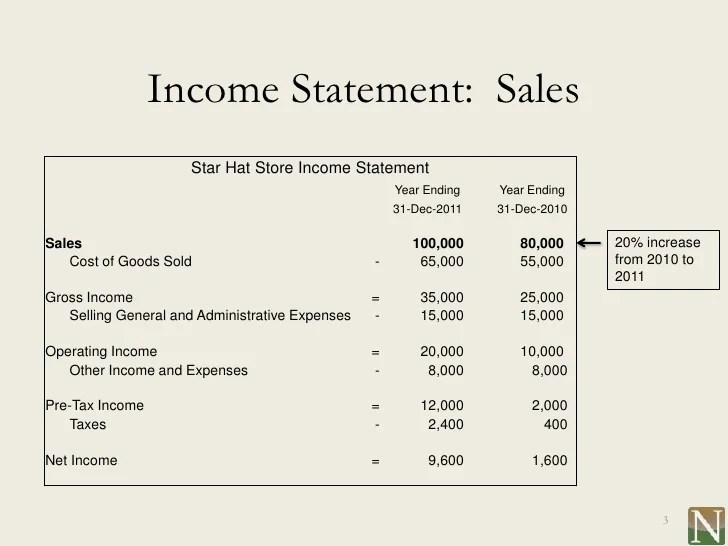
Introduction to Income Statements
An income statement, also known as a profit and loss statement, is a financial document that shows a company’s revenues and expenses during a specific period of time.
The purpose of an income statement is to provide a snapshot of a company’s financial performance, highlighting whether the company is making a profit or a loss.
Components of an Income Statement
- Revenue: This is the total amount of money generated from sales of goods or services.
- Expenses: These are the costs incurred in the process of generating revenue, such as salaries, rent, utilities, and supplies.
- Net Income: This is the total revenue minus total expenses, indicating the company’s profit or loss.
- Gross Profit: This is the revenue minus the cost of goods sold, showing the profitability of the core business operations.
- Operating Income: This is the income generated from the company’s primary business activities, excluding interest and taxes.
Importance of Understanding Income Statements
Income statements are crucial financial documents that provide valuable insights into a company’s profitability and overall financial performance. Understanding income statements is essential for businesses to make informed decisions, set realistic goals, and plan for the future effectively.
Financial Decision-Making
Income statements play a vital role in financial decision-making by providing a clear picture of a company’s revenue, expenses, and net income over a specific period. For example, when analyzing an income statement, businesses can identify trends in revenue growth, pinpoint areas of high expenses, and assess the overall profitability of different product lines or services. This information helps businesses make strategic decisions regarding cost-cutting measures, pricing strategies, and investment opportunities.
Assessing Financial Health
Income statements are also used to evaluate a company’s financial health and performance. By examining key financial metrics such as gross profit margin, operating income, and net income, businesses can gauge their profitability and efficiency. For instance, a declining trend in net income over several quarters may indicate operational inefficiencies or decreasing demand for products/services. On the other hand, a consistent increase in gross profit margin could signal successful cost management or pricing strategies. By regularly analyzing income statements, businesses can proactively address financial challenges and capitalize on growth opportunities.
Reading and Analyzing Income Statements
Understanding how to read an income statement effectively is crucial for analyzing a company’s financial performance. By examining key metrics and ratios derived from income statements, you can gain valuable insights into a company’s profitability, operating efficiency, and overall financial health.
Key Metrics and Ratios
- Net Profit Margin: Calculated by dividing net income by total revenue, this ratio indicates the percentage of revenue that translates into profit. A higher net profit margin signifies better profitability.
- Operating Margin: This ratio shows the percentage of revenue left after covering operating expenses. A higher operating margin indicates efficient cost management.
- Return on Assets (ROA): ROA measures how effectively a company is using its assets to generate profit. It is calculated by dividing net income by average total assets.
Interpreting Trends and Anomalies
- Revenue Growth: Analyzing trends in revenue growth over multiple periods can indicate the company’s sales performance. A consistent upward trend is a positive sign.
- Cost Fluctuations: Sudden spikes in operating expenses or cost of goods sold may point to inefficiencies or unexpected challenges in the company’s operations.
- Profitability Changes: Significant fluctuations in net profit margin or operating margin should be investigated to understand the reasons behind the changes.
Common Mistakes in Interpreting Income Statements
When it comes to analyzing income statements, there are some common errors that people tend to make. These mistakes can have a significant impact on decision-making processes within a business. By understanding these common pitfalls, you can improve your financial analysis skills and make more informed decisions based on accurate data.
1. Neglecting Non-Recurring Items
- One common mistake is overlooking non-recurring items such as one-time gains or losses.
- These items can distort the true financial performance of a company if not properly identified and adjusted for.
- Tip: Always carefully review the income statement for any non-recurring items and assess their impact on the overall financial health of the business.
2. Focusing Solely on Net Income
- Another mistake is solely focusing on net income without considering other important metrics such as gross profit margin or operating income.
- Net income alone may not provide a comprehensive picture of a company’s financial performance.
- Tip: Look at multiple metrics in conjunction with net income to get a more holistic view of the company’s profitability.
3. Ignoring Changes in Accounting Policies
- Changes in accounting policies can significantly impact the numbers reported on an income statement.
- Failure to account for these changes can lead to misinterpretation of financial results.
- Tip: Always be aware of any changes in accounting policies and adjust your analysis accordingly to ensure accurate interpretation.
4. Misunderstanding Revenue Recognition
- Incorrectly recognizing revenue can distort the true financial performance of a company.
- Improper revenue recognition practices can lead to inflated revenue figures and misrepresentation of financial health.
- Tip: Understand the principles of revenue recognition and ensure that revenue is being recognized accurately and in accordance with accounting standards.
Using Income Statements for Forecasting and Planning
Income statements play a crucial role in financial forecasting, strategic planning, budgeting, and setting financial goals. By analyzing the information provided in income statements, businesses can make informed decisions about their future financial performance.
Financial Forecasting
Income statements provide a historical record of a company’s financial performance, including revenue, expenses, and net income. By examining trends and patterns from past income statements, businesses can forecast future revenue and expenses. This enables companies to anticipate potential challenges, identify opportunities for growth, and make strategic decisions to achieve their financial goals.
- Forecasting revenue: By analyzing past income statements, businesses can project future sales and revenue streams. This information is crucial for developing sales targets, setting marketing budgets, and assessing the overall financial health of the company.
- Estimating expenses: Income statements also help in estimating future expenses such as operating costs, salaries, and overhead expenses. By accurately predicting expenses, businesses can create realistic budgets and allocate resources effectively.
Strategic Planning
Income statements are essential for strategic planning as they provide valuable insights into a company’s financial performance and profitability. By understanding the components of an income statement, businesses can develop strategies to improve profitability, increase efficiency, and achieve long-term growth.
| Example: | Impact on Strategic Planning |
|---|---|
| Identifying cost-saving opportunities | By analyzing expense categories on the income statement, businesses can identify areas where costs can be reduced or eliminated to improve profitability. |
| Assessing revenue streams | Income statements help businesses evaluate the performance of different revenue streams and focus on strategies to maximize profitable revenue sources. |
Budgeting and Financial Goals
Income statements aid in budgeting by providing a clear picture of a company’s financial performance and cash flow. By using income statements to track revenue and expenses, businesses can create detailed budgets that align with their financial objectives and strategic priorities.
Setting SMART financial goals (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) based on income statement analysis helps businesses stay focused and accountable for their financial performance.