Options trading explained for beginners dives into the world of trading options, breaking down complex concepts into easy-to-understand terms for those new to the game. Get ready to explore the ins and outs of this exciting market!
Introduction to Options Trading
Options trading is a type of financial derivative that gives investors the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an asset at a specified price before a certain date.
Options Contracts
An options contract is an agreement between a buyer and a seller to buy or sell an asset at a specific price within a certain timeframe. The buyer pays a premium to the seller for this right.
Call and Put Options
- A call option gives the holder the right to buy an asset at a specified price within a certain timeframe.
- A put option gives the holder the right to sell an asset at a specified price within a certain timeframe.
Basics of Options Trading
Options trading is a type of investment strategy in the financial markets where traders can buy or sell the right to buy or sell a specific asset at a set price within a specified period. It offers flexibility and leverage for investors looking to manage risk or speculate on market movements.
How Options Trading Works
Options trading involves two types of participants: buyers and sellers. Buyers purchase options contracts, which give them the right to buy (call option) or sell (put option) an asset at a predetermined price before the expiration date. Sellers, on the other hand, are obligated to fulfill the terms of the contract if the buyer decides to exercise their option.
Role of Buyers and Sellers
- Buyers: Pay a premium for the option contract and have the choice to exercise it if it’s profitable.
- Sellers: Receive the premium from the buyer and must be prepared to fulfill the contract if the buyer decides to exercise their option.
Significance of Expiration Dates
Expiration dates play a crucial role in options trading as they determine the timeframe within which the option contract is valid. Once the expiration date passes, the option contract becomes worthless, and traders must decide whether to exercise their rights or let the contract expire.
Types of Options
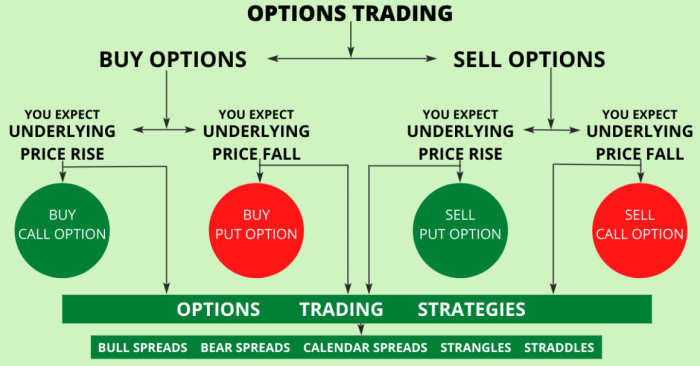
When it comes to options trading, there are different types of options that traders can choose from based on their preferences and risk tolerance. Let’s take a look at the various types of options available in the market.
American vs. European Options
American options can be exercised at any time before the expiration date, giving the holder more flexibility. On the other hand, European options can only be exercised at the expiration date itself. This key difference can impact the trading strategies and decision-making process for traders.
Vanilla Options
Vanilla options are the most basic type of options that involve the buying or selling of a standard call or put option contract. These options are standardized and traded on major exchanges, making them easily accessible to traders. They provide a straightforward way to participate in the options market without complex features or structures.
Exotic Options
Exotic options are more complex and customized options that have non-standard features compared to vanilla options. These options can have unique characteristics such as barrier options, binary options, and Asian options. Exotic options are tailored to specific trading needs and can offer alternative risk management strategies for traders looking for more sophisticated options trading opportunities.
Key Terminology in Options Trading: Options Trading Explained For Beginners
In options trading, there are several key terms that beginners need to understand in order to navigate the market effectively. Let’s break down some of the most important terms below.
Strike Price, Options trading explained for beginners
The strike price of an option is the price at which the option holder can buy or sell the underlying asset. It is the predetermined price at which the option contract can be exercised.
Premium
The premium is the price that the option buyer pays to the option seller for the right to buy or sell the underlying asset. It is essentially the cost of the option contract.
Intrinsic Value
The intrinsic value of an option is the difference between the current price of the underlying asset and the strike price of the option. It represents the real value of the option if it were to be exercised immediately.
In-the-Money, At-the-Money, and Out-of-the-Money Options
- In-the-Money: An option is considered in-the-money if it has intrinsic value. For call options, this means the current price of the underlying asset is higher than the strike price. For put options, it means the current price is lower than the strike price.
- At-the-Money: At-the-money options have a strike price that is equal to the current price of the underlying asset. They have no intrinsic value.
- Out-of-the-Money: Out-of-the-money options have no intrinsic value. For call options, the current price is lower than the strike price, and for put options, the current price is higher than the strike price.
Implied Volatility
Implied volatility is a measure of how much the market expects the price of the underlying asset to fluctuate in the future. It is a key factor in determining the price of options, as higher implied volatility generally leads to higher option premiums.
Strategies in Options Trading
When it comes to options trading, having a solid strategy in place is crucial for success. Let’s dive into some common options trading strategies and how to implement them effectively.
Covered Calls
Covered calls are a popular strategy where an investor sells a call option on a stock they already own. This strategy can generate income from the premium received, while also potentially allowing for some profit if the stock price remains stable or rises slightly.
Protective Puts
Protective puts involve buying a put option to protect against a decline in the price of a stock you own. This strategy acts as insurance, limiting potential losses if the stock price drops significantly.
Bullish Strategies
Bullish strategies involve using options to capitalize on an anticipated rise in the price of a stock. This can be achieved through strategies like buying call options or implementing a bull call spread.
Bearish Strategies
Conversely, bearish strategies are used when an investor expects a stock’s price to decrease. Strategies like buying put options or implementing a bear put spread can be utilized to profit from a declining stock price.
Risk Management
Risk management is essential in options trading to protect against potential losses. Strategies like setting stop-loss orders, diversifying your portfolio, and using options as a hedge can help mitigate risk and preserve capital.