Product Pricing Strategies sets the stage for businesses to thrive by exploring innovative approaches to pricing products. From cost-based to value-based and psychological tactics, this dynamic discussion unveils the secrets to driving sales and revenue growth.
Introduction to Product Pricing Strategies
In the world of business, product pricing strategies play a crucial role in determining the success of a company. These strategies involve setting the right price for a product or service to attract customers and generate revenue. Let’s dive into the importance of product pricing strategies and how they can impact sales and revenue.
Product pricing strategies can have a significant impact on a company’s bottom line. By setting the right price, businesses can attract customers, increase sales, and maximize profit margins. On the other hand, pricing products too high or too low can lead to decreased sales and revenue.
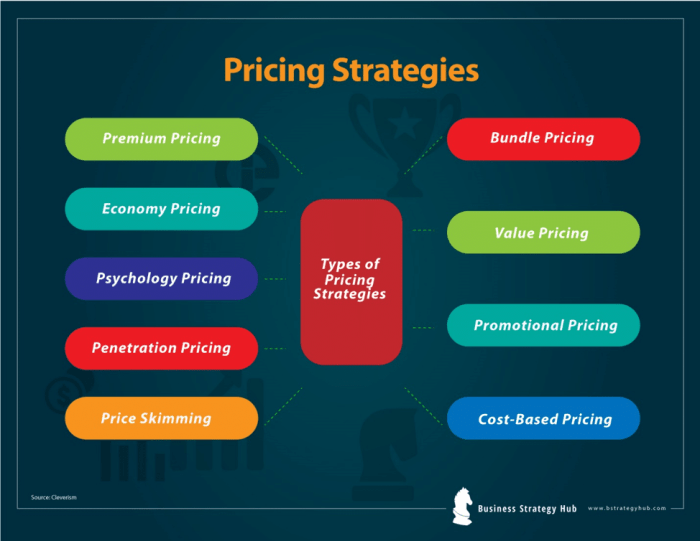
Types of Product Pricing Strategies
- Penetration Pricing: Setting a low initial price to attract customers and gain market share.
- Price Skimming: Setting a high price initially and then gradually lowering it over time.
- Competitive Pricing: Setting prices based on competitors’ prices to stay competitive in the market.
- Value-Based Pricing: Setting prices based on the perceived value of the product or service to the customer.
Cost-Based Pricing
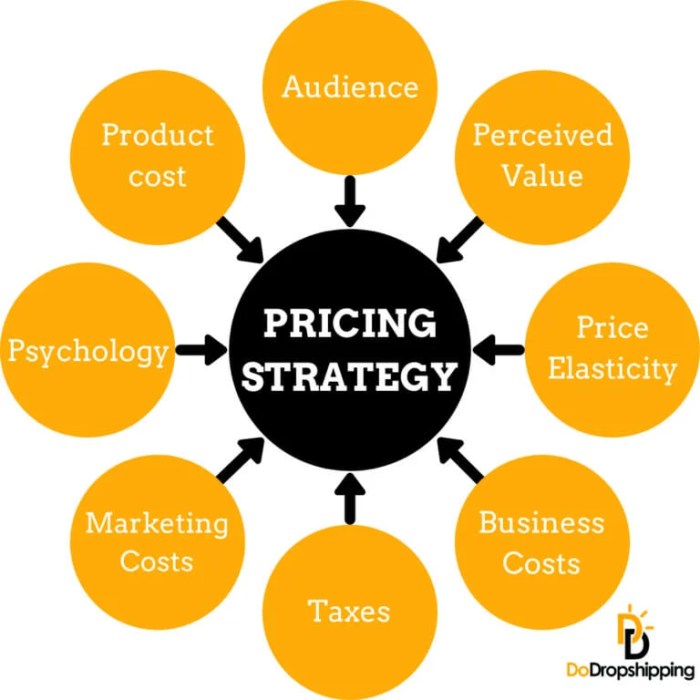
Cost-based pricing is a pricing strategy where a company determines the selling price of a product by considering the production cost and adding a markup to ensure a profit margin. The calculation involves adding up all the costs associated with producing the product, including direct costs like materials and labor, as well as indirect costs like overhead expenses. Once the total cost is determined, a markup percentage is added to set the final selling price.
Advantages of Cost-Based Pricing
- Easy to calculate: Cost-based pricing is straightforward and easy to calculate, making it a simple method for small businesses or new companies.
- Ensures profitability: By including all costs in the pricing calculation, companies can ensure that they are making a profit on each product sold.
- Provides a baseline: Cost-based pricing sets a baseline for pricing decisions, allowing companies to adjust prices based on market conditions or competition.
Disadvantages of Cost-Based Pricing
- Does not consider customer demand: Cost-based pricing does not take into account customer perceptions of value or willingness to pay, potentially leading to overpricing or underpricing.
- May not reflect market conditions: Prices set solely based on costs may not be competitive in the market, especially if competitors are using different pricing strategies.
- Limits flexibility: Relying solely on costs for pricing may limit the company’s ability to adjust prices based on changing market dynamics or demand fluctuations.
Companies Using Cost-Based Pricing
- McDonald’s: The fast-food giant often uses cost-based pricing to set menu prices, ensuring that each item covers the cost of production and includes a profit margin.
- Utility companies: Companies providing essential services like electricity or water often use cost-based pricing to cover operating expenses and ensure sustainability.
- Construction companies: Builders and contractors typically calculate project costs and add a markup to determine the final price for construction projects, using cost-based pricing.
Value-Based Pricing
Value-based pricing is a strategy where companies set the price of their products based on the perceived value to the customer rather than the cost of production. This approach focuses on the benefits and value that the product provides to the customer, allowing companies to capture a greater share of the value they create.
Companies determine the value of their products for pricing by conducting market research, analyzing customer preferences, and understanding the competitive landscape. By identifying the unique selling points of their products and the benefits they offer to customers, companies can assess how much value customers place on their offerings.
Comparison with Other Pricing Strategies
Value-based pricing differs from cost-based pricing, where prices are set by adding a markup to the cost of production, and competitor-based pricing, where prices are influenced by what competitors are charging. Unlike these strategies, value-based pricing focuses on the perceived value of the product to the customer, allowing companies to capture a higher price if the product is perceived as delivering superior benefits.
- Value-based pricing takes into account the customer’s willingness to pay based on the value they receive, while cost-based pricing relies solely on the production costs.
- Unlike competitor-based pricing, value-based pricing is more customer-centric and focuses on the unique value proposition of the product.
- Value-based pricing allows companies to differentiate their products based on the value they provide rather than engaging in price wars with competitors.
Competition-Based Pricing
Competition-based pricing is a strategy where companies set their prices based on what their competitors are charging for similar products or services. By analyzing the pricing strategies of competitors, companies can adjust their own prices to stay competitive in the market.
Analyzing Competitors for Pricing
When analyzing competitors for pricing, companies typically look at factors such as the quality of the product, target market, branding, and overall value proposition. By understanding how competitors position themselves in the market, companies can determine where they fit in and how they can differentiate themselves through pricing.
- Companies often conduct market research to gather data on competitor pricing strategies.
- They may also analyze customer feedback and reviews to understand how pricing impacts consumer perception.
- Using tools like pricing software and competitive analysis reports can help companies track changes in competitor pricing over time.
Successful Implementation Examples
One example of successful implementation of competition-based pricing is in the airline industry. Airlines often adjust their ticket prices based on what competitors are charging for similar routes. This dynamic pricing strategy allows airlines to remain competitive and maximize revenue based on market demand.
Another example is in the retail sector, where companies like Walmart and Target regularly monitor competitor prices and offer price matching to ensure they are providing the best value to customers. This strategy helps these companies retain customers and stay ahead of the competition in a crowded market.
Psychological Pricing Strategies
When it comes to pricing strategies, psychology plays a crucial role in influencing consumer behavior. By understanding how consumers perceive prices, businesses can strategically set prices to maximize sales and profitability.
Odd-Even Pricing
Odd-even pricing is a strategy where prices are set at odd numbers (e.g. $9.99) instead of round numbers (e.g. $10). This pricing tactic gives consumers the perception that they are getting a better deal, even though the difference is minimal. It creates a psychological effect where the price seems lower than it actually is, leading to increased sales.
Bundle Pricing
Bundle pricing involves offering multiple products or services for a lower combined price than if purchased separately. This strategy appeals to consumers by providing perceived value and savings. Customers are more likely to make a purchase when they feel they are getting a good deal, even if they end up buying more than they initially planned.
Psychological Pricing and Consumer Behavior
Psychological pricing tactics can greatly influence consumer behavior. By leveraging strategies like odd-even pricing and bundle pricing, businesses can attract more customers, increase sales volume, and create a positive perception of their products or services. These pricing techniques tap into the psychology of consumers, playing on their emotions and perceptions to drive purchase decisions.
Case Studies, Product Pricing Strategies
– Apple: Apple often uses odd-even pricing in its product lineup, pricing items at $499 instead of $500. This slight difference in price can make a significant impact on consumer perception and purchasing behavior.
– Amazon: Amazon frequently utilizes bundle pricing by offering discounts on bundled products, encouraging customers to buy more items. This strategy has contributed to Amazon’s success in increasing average order value and customer loyalty.